2 x E1 G.703 TDM over IP/Ethernet converter / multiplexer – mini type casing, supporting Point to Multipoint feature
2 x E1 G.703 TDM over IP | E1 over IP | E1 to Ethernet converter | mini type unit for applications where 2 E1 is needed and installation space is limited and PMP - Point to Multipoint feature support is needed
- User-friendly Web server supported for easy setup and maintenance
- Support SNMP V1 and V2 network management
- Point to point and point to multipoint supported
- Uplink ports 1+1 backup supported
- AN-TDM-IP-2E1 provide 2 E1 Ports
- Stable E1 clock recovery, low jitter and wander
- Low processing delay for E1 channels, high bandwidth usage efficiency
- Resist to packet loss, with PCM frame synchronization protection
- User definable encapsulation packet size for different application
- Support Ethernet encapsulation and UDP/IP protocol encapsulation
- Support VLAN settings for E1 service and in band VLAN management.
- Enough jitter buffer to resist packet delay variation (PDV)
- Local and remote E1 LOS and AIS and packet loss indication for trouble-shooting and maintenance
- Hardware and software program online upgrade
Capacity
It supports 1 E1 port, two 10/100Base-Tx uplink Ethernet ports.
E1 interface
Comply with ITU-T G.703 recommendation
E1 port impedance E1-120Ω for twisted pair cables or 75Ω for coax (The RJ45 E1-120Ω are default for ports)
End-to-end delay (minimum delay setting) £ 10ms
Output frequency offset (adaptive timing, stabilized) £5 ppm
Output jitter (adaptive timing) £ 0.1UI
10/100Base-Tx port
Comply with IEEE 802.3
10M/100M Adaptive
Half/Full Duplex Adaptive
Support 802.1Q MAC
Uplink ports 1+1 backup supported
Two user data ports supported. And Web manager supported through anyone of two user data ports.
Power
AC: 100V~260V/50Hz (fuse: 1A)
DC: -38V ~ -62V (optional)
Power Consumption: ≤4W
Operating condition
Temperature: (0~45) ℃
Humidity: ≤90% (non-condensing)
Dimensions
Width × Height × Depth: 185×35×138 mm
Weight
≤ 1 kg
Example of web manager screen is below:
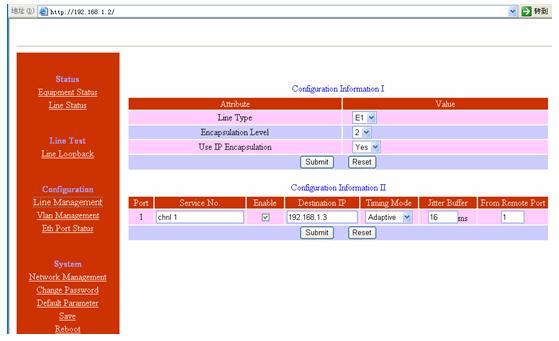
Configuration examples:

| AN-TDM-IP-2E1/A | E1 to Ethernet converter / multiplexer (TDM over IP) ,with 2-port E1 and 2-port 10/100Base-T interfaces for downlink, 1+1 ports 10/100Base-T interfaces for uplink, 75ohm/120ohm optional, DC-48V or AC220V |
Description
AN-TDM-IP-2E1/A is used to setup 2 transparent E1’s channel over LAN or IP networks
The AN-TDM-IP-2E1/A has many optional parameters, which can be modified by the user to suite different application requirements. Please read this manual carefully before installing the product.
It is well known that the E1 signal comes from PCM technology which is TDM in nature. It transmits information in a constant bit rate of E1_2048kbit/s, TDM technology occupies fixed transmission bandwidth, with QoS features suitable for real-time applications such as voice and video. The QoS features include short and stable transmission delay, low jitter and wander, etc.
The most widely used application of AN-TDM-IP-2E1/A is to set up point to point wireless E1 links using low cost wireless LAN bridges. AN-TDM-IP-2E1/A can work with most LAN bridges on the market.
Until recently, voice and data were, and still are to a large extent, transported over two separate networks. But the requirement for both types of information to be carried over a unified network is growing rapid. Packets over SONET/SDH techniques to integrate date into the TDM network have been around for many years. But for voice over packet based data networks, most of the efforts are spent on creating special equipment that packets voice or video signals, such as VoIP techniques.
The AN-TDM-IP-2E1/A can be used to emulate transparent E1 channels over an Ethernet with adequate QoS, so that most of the existing E1 based applications can be readily setup over Ethernet LANs and WANs. One particular suited application is to build E1 links with low cost wireless LAN bridges, replacing much more costly microwave radios.
Both Web Server and SNMP management are supported through anyone of two Ethernet ports of AN-TDM-IP. The management has four sections: Status, Line Test, Configuration and System.

