Admission of users to a shared upstream channel with resolution/avoidance of contention is called medium access. It is required for connection-oriented or connectionless communication which are having prior establishment of a path or not.
Different modes of medium access are developed for different scenarios. Distributed contention access is made so users compete among themselves for bandwidth. Most common methods are Carrier Sense Multiple Access – Collision Detection (CSMA-CD) and Carrier Sense Multiple Access – Collision Avoid (CSMA-CA). First one detects collision and backs off if it happens. Second one is checking before data is sent to avoid collision.
PON, cable data systems, cellular mobile, and WiMAX mostly rely on request-allocation schemes, where OLT provides user with frequency and/or time slot for transmitting data. Allocation can be made even without user request if the management policy defines so. CSMA-CD and CSMA-CA are shown together with request-allocation mode in Figure 1.
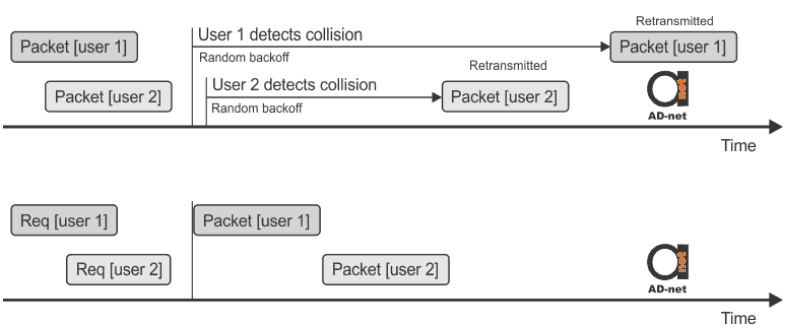
Figure 1. Basic medium access modes of contention access and request-allocation
Priority of data transmission varies based on the type of data. VoIP data requires higher priority, so it may have shorter back-off in shared access system, while request allocation access would provide earlier slot allocations. Most common physical-layer channel sharing technologies are Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA), Time Division Multiple Access (TDMA), and Wavelength Division Multiple Access (WDMA) that are shown in comparison in Table 2.
Table 2. Comparison of Medium Access Technologies
| CDMA | TDMA | WDMA | |
| Pros | High data security | One transceiver at the OLT | High bandwidth |
| No fixes limit on the number of ONUs/ONTs | Easy to add a new ONU/ONT | High data security | |
| Finer granularity than a wavelength | |||
| Cons | High interchannel interference | Needs synchronization | High cost for transmitter array |
| High cost with expensive equipment | Needs bandwidth allocation | Low scalability |
CDMA as an option for PON is relatively expensive. It requires components capable of handling data with much higher rates than the carrier data rate. It is happening due to the encoding that each ONU/ONT signal has with a unique wideband waveform. This method also increases the interchannel interference (ICI) which should be handled by expensive equipment.
TDMA and TDM are the most common solutions for PON in upstream and downstream directions, respectively. ONUs/ONTs in the network are having time slots for each, like in the second part of Figure 1. This allows great scalability for the network, since it could be easily extended.
WDMA is using different wavelength for each ONU/ONT in the network. Bandwidth of specific user line is defined by capacity of wavelength channel. This system requires complex OLT equipment – multiwavelength transmitter.


